The oem package provides estimation for various penalized linear models using the Orthogonalizing EM algorithm. Documentation for the package can be found here: oem site.
Install using the devtools package (RcppEigen must be installed first as well):
devtools::install_github("jaredhuling/oem")or by cloning and building using R CMD INSTALL
To cite oem please use:
Xiong, S., Dai, B., Huling, J., Qian, P. Z. G. (2016) Orthogonalizing
EM: A design-based least squares algorithm, Technometrics, Volume 58,
Pages 285-293,
http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/00401706.2015.1054436.
Huling, J.D. and Chien, P. (2018), Fast Penalized Regression and Cross Validation for Tall Data with the OEM Package, Journal of Statistical Software, to appear, URL: https://arxiv.org/abs/1801.09661.
library(microbenchmark)
library(glmnet)
library(oem)
# compute the full solution path, n > p
set.seed(123)
n <- 1000000
p <- 100
m <- 25
b <- matrix(c(runif(m), rep(0, p - m)))
x <- matrix(rnorm(n * p, sd = 3), n, p)
y <- drop(x %*% b) + rnorm(n)
lambdas = oem(x, y, intercept = TRUE, standardize = FALSE, penalty = "elastic.net")$lambda[[1]]
microbenchmark(
"glmnet[lasso]" = {res1 <- glmnet(x, y, thresh = 1e-10,
standardize = FALSE,
intercept = TRUE,
lambda = lambdas)},
"oem[lasso]" = {res2 <- oem(x, y,
penalty = "elastic.net",
intercept = TRUE,
standardize = FALSE,
lambda = lambdas,
tol = 1e-10)},
times = 5
)## Unit: seconds
## expr min lq mean median uq max neval cld
## glmnet[lasso] 5.325385 5.374823 5.859432 6.000302 6.292411 6.304239 5 a
## oem[lasso] 1.539320 1.573569 1.600241 1.617136 1.631450 1.639730 5 b# difference of results
max(abs(coef(res1) - res2$beta[[1]]))## [1] 1.048243e-07res1 <- glmnet(x, y, thresh = 1e-12,
standardize = FALSE,
intercept = TRUE,
lambda = lambdas)
# answers are now more close once we require more precise glmnet solutions
max(abs(coef(res1) - res2$beta[[1]]))## [1] 3.763507e-09library(sparsenet)
library(ncvreg)
# compute the full solution path, n > p
set.seed(123)
n <- 5000
p <- 200
m <- 25
b <- matrix(c(runif(m, -0.5, 0.5), rep(0, p - m)))
x <- matrix(rnorm(n * p, sd = 3), n, p)
y <- drop(x %*% b) + rnorm(n)
mcp.lam <- oem(x, y, penalty = "mcp",
gamma = 2, intercept = TRUE,
standardize = TRUE,
nlambda = 200, tol = 1e-10)$lambda[[1]]
scad.lam <- oem(x, y, penalty = "scad",
gamma = 4, intercept = TRUE,
standardize = TRUE,
nlambda = 200, tol = 1e-10)$lambda[[1]]
microbenchmark(
"sparsenet[mcp]" = {res1 <- sparsenet(x, y, thresh = 1e-10,
gamma = c(2,3), #sparsenet throws an error
#if you only fit 1 value of gamma
nlambda = 200)},
"oem[mcp]" = {res2 <- oem(x, y,
penalty = "mcp",
gamma = 2,
intercept = TRUE,
standardize = TRUE,
nlambda = 200,
tol = 1e-10)},
"ncvreg[mcp]" = {res3 <- ncvreg(x, y,
penalty = "MCP",
gamma = 2,
lambda = mcp.lam,
eps = 1e-7)},
"oem[scad]" = {res4 <- oem(x, y,
penalty = "scad",
gamma = 4,
intercept = TRUE,
standardize = TRUE,
nlambda = 200,
tol = 1e-10)},
"ncvreg[scad]" = {res5 <- ncvreg(x, y,
penalty = "SCAD",
gamma = 4,
lambda = scad.lam,
eps = 1e-7)},
times = 5
)## Unit: milliseconds
## expr min lq mean median uq
## sparsenet[mcp] 1466.54465 1492.72548 1527.32113 1517.19926 1579.70827
## oem[mcp] 95.71381 98.09740 105.90083 105.76415 110.31668
## ncvreg[mcp] 5196.48035 5541.69429 5669.10010 5611.31491 5865.06723
## oem[scad] 70.74110 71.46554 80.21926 78.76494 84.25458
## ncvreg[scad] 5289.59790 5810.69254 5801.60997 5950.84377 5964.01276
## max neval cld
## 1580.42800 5 a
## 119.61209 5 b
## 6130.94372 5 c
## 95.87013 5 b
## 5992.90288 5 cdiffs <- array(NA, dim = c(2, 1))
colnames(diffs) <- "abs diff"
rownames(diffs) <- c("MCP: oem and ncvreg", "SCAD: oem and ncvreg")
diffs[,1] <- c(max(abs(res2$beta[[1]] - res3$beta)), max(abs(res4$beta[[1]] - res5$beta)))
diffs## abs diff
## MCP: oem and ncvreg 1.725859e-07
## SCAD: oem and ncvreg 5.094648e-08In addition to the group lasso, the oem package offers computation for the group MCP, group SCAD, and group sparse lasso penalties. All aforementioned penalties can also be augmented with a ridge penalty.
library(gglasso)
library(grpreg)
library(grplasso)
# compute the full solution path, n > p
set.seed(123)
n <- 10000
p <- 200
m <- 25
b <- matrix(c(runif(m, -0.5, 0.5), rep(0, p - m)))
x <- matrix(rnorm(n * p, sd = 3), n, p)
y <- drop(x %*% b) + rnorm(n)
groups <- rep(1:floor(p/10), each = 10)
grp.lam <- oem(x, y, penalty = "grp.lasso",
groups = groups,
nlambda = 100, tol = 1e-10)$lambda[[1]]
microbenchmark(
"gglasso[grp.lasso]" = {res1 <- gglasso(x, y, group = groups,
lambda = grp.lam,
intercept = FALSE,
eps = 1e-8)},
"oem[grp.lasso]" = {res2 <- oem(x, y,
groups = groups,
intercept = FALSE,
standardize = FALSE,
penalty = "grp.lasso",
lambda = grp.lam,
tol = 1e-10)},
"grplasso[grp.lasso]" = {res3 <- grplasso(x=x, y=y,
index = groups,
standardize = FALSE,
center = FALSE, model = LinReg(),
lambda = grp.lam * n * 2,
control = grpl.control(trace = 0, tol = 1e-10))},
"grpreg[grp.lasso]" = {res4 <- grpreg(x, y, group = groups,
eps = 1e-10, lambda = grp.lam)},
times = 5
)## Unit: milliseconds
## expr min lq mean median uq
## gglasso[grp.lasso] 679.59049 724.16350 858.99280 801.79179 865.83580
## oem[grp.lasso] 59.84769 62.23879 64.11779 63.36026 64.30146
## grplasso[grp.lasso] 3714.92601 3753.18663 4322.32431 4537.50185 4786.80867
## grpreg[grp.lasso] 1216.21794 1248.84647 1270.46132 1269.71047 1287.75969
## max neval cld
## 1223.58241 5 a
## 70.84075 5 b
## 4819.19839 5 c
## 1329.77201 5 adiffs <- array(NA, dim = c(2, 1))
colnames(diffs) <- "abs diff"
rownames(diffs) <- c("oem and gglasso", "oem and grplasso")
diffs[,1] <- c( max(abs(res2$beta[[1]][-1,] - res1$beta)), max(abs(res2$beta[[1]][-1,] - res3$coefficients)) )
diffs## abs diff
## oem and gglasso 1.303906e-06
## oem and grplasso 1.645871e-08set.seed(123)
n <- 500000
p <- 200
m <- 25
b <- matrix(c(runif(m, -0.5, 0.5), rep(0, p - m)))
x <- matrix(rnorm(n * p, sd = 3), n, p)
y <- drop(x %*% b) + rnorm(n)
groups <- rep(1:floor(p/10), each = 10)
# fit all group penalties at once
grp.penalties <- c("grp.lasso", "grp.mcp", "grp.scad",
"grp.mcp.net", "grp.scad.net",
"sparse.group.lasso")
system.time(res <- oem(x, y,
penalty = grp.penalties,
groups = groups,
alpha = 0.25, # mixing param for l2 penalties
tau = 0.5)) # mixing param for sparse grp lasso ## user system elapsed
## 2.043 0.222 2.267The oem algorithm is quite efficient at fitting multiple penalties simultaneously when p is not too big.
set.seed(123)
n <- 100000
p <- 100
m <- 15
b <- matrix(c(runif(m, -0.25, 0.25), rep(0, p - m)))
x <- matrix(rnorm(n * p, sd = 3), n, p)
y <- drop(x %*% b) + rnorm(n)
microbenchmark(
"oem[lasso]" = {res1 <- oem(x, y,
penalty = "elastic.net",
intercept = TRUE,
standardize = TRUE,
tol = 1e-10)},
"oem[lasso/mcp/scad/ols]" = {res2 <- oem(x, y,
penalty = c("elastic.net", "mcp",
"scad", "grp.lasso",
"grp.mcp", "sparse.grp.lasso",
"grp.mcp.net", "mcp.net"),
gamma = 4,
tau = 0.5,
alpha = 0.25,
groups = rep(1:10, each = 10),
intercept = TRUE,
standardize = TRUE,
tol = 1e-10)},
times = 5
)## Unit: milliseconds
## expr min lq mean median uq max
## oem[lasso] 125.6408 126.7870 130.3534 127.3374 133.4962 138.5055
## oem[lasso/mcp/scad/ols] 148.3162 152.1743 153.0176 152.4529 154.4300 157.7144
## neval cld
## 5 a
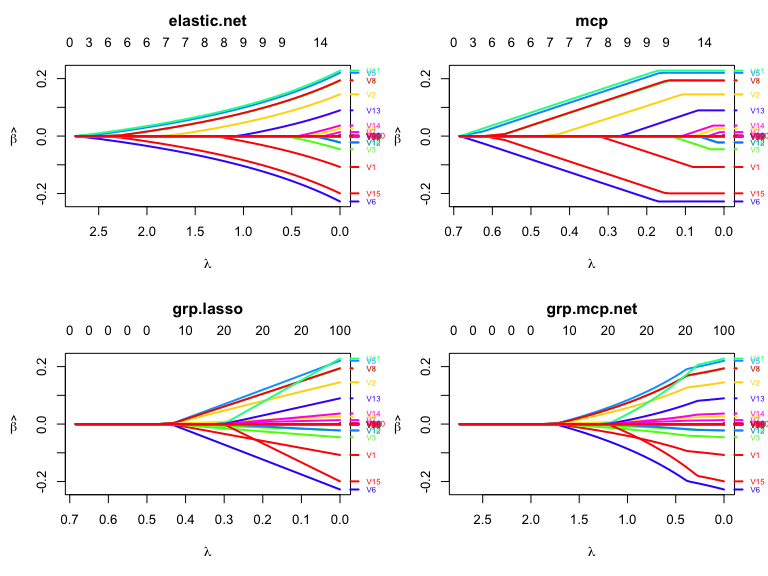
## 5 b#png("../mcp_path.png", width = 3000, height = 3000, res = 400);par(mar=c(5.1,5.1,4.1,2.1));plot(res2, which.model = 2, main = "mcp",lwd = 3,cex.axis=2.0, cex.lab=2.0, cex.main=2.0, cex.sub=2.0);dev.off()
#
layout(matrix(1:4, ncol=2, byrow = TRUE))
plot(res2, which.model = 1, lwd = 2,
xvar = "lambda")
plot(res2, which.model = 2, lwd = 2,
xvar = "lambda")
plot(res2, which.model = 4, lwd = 2,
xvar = "lambda")
plot(res2, which.model = 7, lwd = 2,
xvar = "lambda")